Color models explain how colors are defined and when creating slides you need to know how to define RGB colors, how to utilize the HSL values to adjust colors to your advantage and how brand CMYK values and web HEX values relates to the colors you need to use in PowerPoint and how to “translate” them for use in PowerPoint.
Before we talk about the different color models, let’s talk about the anatomy of colors.
The anatomy of colors
A color can be pure, have a lightness/darkness, and have a intensity. The pure or true color, the identity of a color (“red”) is called hue. It’s also a way to describe the color on the color wheel (“orange-red”). The color value refers to the lightness (added white) or darkness (added dark) of a color. Value is also referred to as “tone” or “luminance”. Saturation is the intensity of a hue. It is also called chroma. A hue is most intense when it is fully saturated. When it is less saturated it is dull or muted. The most important of the three is value as neither a hue or saturation can exist without a value.

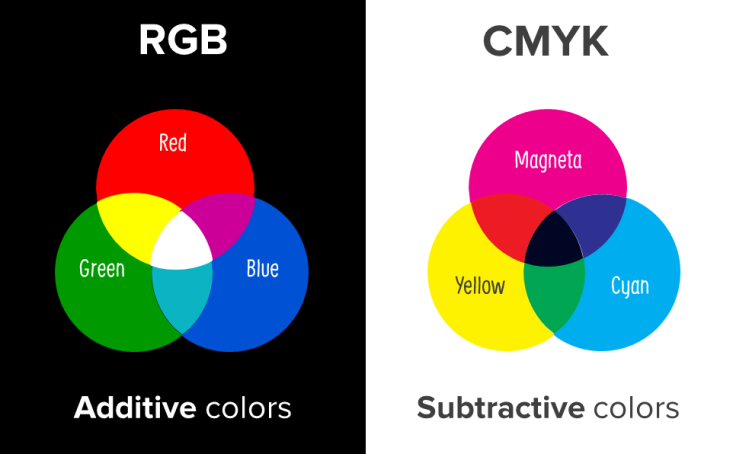
The color of light behaves differently than the color of pigment. Additive colors are the colors of lights and subtractive colors are the colors of pigment, paints and ink – the physical media.

Two main color models are based on the concept of additive and subtractive colors. Additive colors – colors with lights – use the primary colors red, green and blue (or RGB for short). Subtractive colors – colors with pigments – use the primary colors cyan, magenta, yellow and key/black (or CMYK for short).
When using the RGB model you mix equal proportiosn of red and green “light” to create yellow. When using the CMYK model you mix equal proportions of yellow and cyan (blue) “paint” to create green.
Model #1 The RGB color model
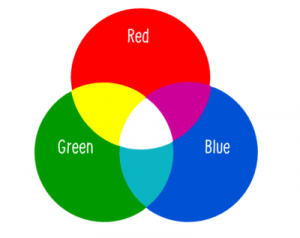 The RGB color model is based on the additive mixture of three monochromatic lights – red, green and blue – and the ability to create all other colors by combining these colors. RGB colors are composed of combinations of portions of red, green and blue light beams that goes straight from a screen into your eyes.
The RGB color model is based on the additive mixture of three monochromatic lights – red, green and blue – and the ability to create all other colors by combining these colors. RGB colors are composed of combinations of portions of red, green and blue light beams that goes straight from a screen into your eyes.
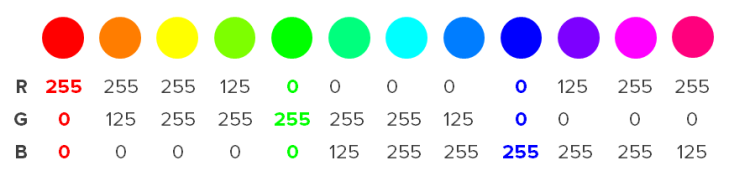
How to create colors with RGB?
The RGB model combine parts of the three primary colors red, green and blue. Each of the primary colors can have a value in the range from 0 to 255. PowerPoint use the RGB model to show colors for presentations as these are supposedly created to be shown on a projector using light.
Model #2: The CMYK color model
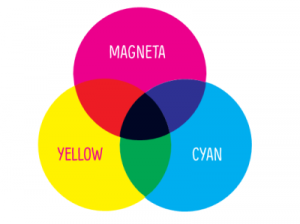 The CMYK model is a subtractive model using blue (cyan), red (magneta) and yellow to mix all colors and adds black (key) as a fourth color. CMYK colors are used specifically for printed material and physical media and are created by combinations of the primary colors almost like blending colors on white paper.
The CMYK model is a subtractive model using blue (cyan), red (magneta) and yellow to mix all colors and adds black (key) as a fourth color. CMYK colors are used specifically for printed material and physical media and are created by combinations of the primary colors almost like blending colors on white paper.
How to create colors with CMYK?
The CMYK model combines values of the primary colors cyan, magenta, yellow – and black. Each of the colors are calculated in percentages – from 0 to 100%. Vector software such as Illustrator use the CMYK model as this is used to create material to be physically printed.
Model #3: The HSL color model
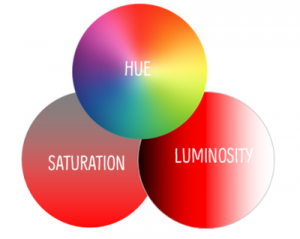 The HSL color model is a subset of the RGB model that expresses the colors in terms of hue, saturation and luminosity. HSL tries to bridge the RGB color model, understood by computers, to mix colors more like humans do.
The HSL color model is a subset of the RGB model that expresses the colors in terms of hue, saturation and luminosity. HSL tries to bridge the RGB color model, understood by computers, to mix colors more like humans do.
Luminosity: An original hue have a luminosity value of 128. When you decrease this value (minimum is 000) the color becomes darker (shade). When you increase this value (maximum is 255) the color becomes brighter (tint).
Saturation: An original hue is fully saturated/vibrant and have a saturation level of 255 (maximum). When saturation is decreased (minimum is 000) the color is almost gone and it becomes desaturated/neutralized).
Hue: The pure color, hue, can be calculated by giving it a number between 0 to 255 where pure red has a hue of 0. If you change just the hue value, the new hue will have the same saturation and luminosity values as the original color.
How to create colors with HSL*?
The HSL model combine values of a color’s hue, saturation and luminosity. Each of the three parts can have a value in the range from 0 to 255. PowerPoint has its version of the HSL-model built in to offer a way to adjust colors. Using the HSL model and adjusting hue, saturation and luminosity, you can fix bad automatically generated tints/shade colors in PowerPoint.
(*as used in PowerPoint)

Model #4: The HEX color model
The HEX color model is an extension of the RGB model but using hexadecimal numbers to define colors used when defining color in HTML code. HEX is used specifically for online material and websites and use combinations of the primary colors similar to RGB.
How to create colors with HEX?
The HEX color model combines parts of the three primary colors red, green and blue. Each of the primary colors can have a value in the range 00 (minimum) to FF (maximum) in hexadecimals numbers (numbers that goes from 0 to FF, with 80 being the middle). Corporate websites use the HEX model to define colors used for websites and online applications.
RGB, CMYK, HSL, HEX, hue, saturation, value… are you still with us?

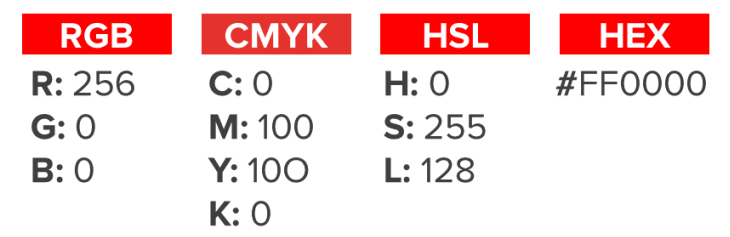
The color red in all four color models
Read the other parts in our Colors for PowerPoint series:
View this post as a slide presentation:


